Epidemiology of Ebola
Epidemiology of Ebola is the study of the distribution and pattern of the disease and its effect on human health. It includes a discussion of the natural history of the disease, the epidemiology and morbidity and mortality of the disease, the factors influencing the spread of the disease and the interventions used to prevent and control the disease. In addition, it describes the societal implications of a disease.
Introduction & Historical Significance
The Ebola virus is a serious disease that causes hemorrhagic fever and death. It is transmitted to humans through contact with body fluids or blood of infected individuals.
Although there have been 34 outbreaks of the disease in Africa since 1976, the largest outbreak has occurred in the past two years, in the west African country of Guinea. There have been over 28,000 confirmed cases and over 11,300 deaths.
This outbreak triggered concern that Ebola could spread to other countries in the region. However, the disease was contained by concerted international action. In mid-January, Liberia announced that it had ended the transmission of the disease. During the first months of 2016, Sierra Leone and Guinea reported continued cases of the disease.
Although the Ebola virus is highly fatal, there are effective ways to prevent and contain the virus. These include antiviral drugs, monoclonal antibodies and vaccines. An efficient case response also plays an important role in ending the outbreak.
The success of EVD control requires a strong workforce, adequate surveillance, efficient laboratory diagnosis, and effective coordination. Also, it is critical to address gaps in the health systems of the affected countries.
Natural Life History
Ebola virus disease, or EVD, is a viral illness that is fatal in many cases. It is a member of the filovirus family and is transmitted from people to others through direct contact with infected body fluids, objects, or animals.
EVD is rare, and outbreaks can occur in isolated areas of Africa. The virus has been documented in wild animals, such as chimpanzees and gorillas. However, domestic animals such as pigs do not play a significant role in the transmission of the virus.
Although the natural reservoir of the Ebola virus has not yet been identified, scientists suspect that fruit bats are the most likely candidate species. These animals carry the virus on their bodies, but do not get sick or exhibit symptoms of acute infection.
The first known case of EVD in humans was reported in 1976. This outbreak occurred in the Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Sudan. Scientists discovered that the SUDV was genetically distinct from Zaire ebolavirus. A second outbreak occurred in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1995, and the Kikwit region was quarantined for a period.
Prevalence Morbidity & Mortality
Currently, 34 outbreaks of Ebola have been reported in 11 countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. They have affected 34 356 people and caused 14 823 deaths.
This massive scale of an ongoing outbreak highlights the urgent need for new treatments. Rapid case identification, effective surveillance and laboratory diagnosis are essential to ending EVD outbreaks. In addition to the challenges associated with detecting and responding to EVD, a number of environmental and sociocultural factors also pose significant challenges to its detection and containment.
The epidemiological features of the EVD epidemic include the high prevalence of urban populations and minimal public health infrastructure. Additionally, the broader contextual factors such as political instability and socioeconomic status can influence health outcomes and thereby the incidence and severity of the disease. It is imperative to conduct more extensive studies to better understand the overall health impacts of the epidemic.
To determine the magnitude of the indirect health effects of the EVD epidemic in West Africa, we conducted a systematic review. Our study focused on the direct and indirect effects of the disease, as well as the health-seeking behavior of the population.
Primary Interventions
Ebola is a highly fatal disease, causing severe illness in both humans and non-human primates. It is a member of the filovirus family. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with the body fluids of an infected person or from an infected animal. Symptoms of the disease include fever, sore throat, and joint pain.
There are three primary interventions in the epidemiology of Ebola: prevention, control, and containment. Each intervention is aimed at limiting the outbreak. Prevention measures include reducing exposure to animals that can transmit the disease. Control measures involve protecting health care workers. They also include identifying people who might have been infected with the virus and preventing the spread of the disease.
Containment involves limiting access to mass gatherings. Individuals who have been exposed to the disease will be monitored for 21 days. During this time, they will be prevented from public transportation. This is a vital step in the control of the outbreak.
In order to reduce the risk of human-to-human transmission, health care workers must wear gloves. They should also avoid handling the body fluids of suspected patients.
Secondary Interventions
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is an infectious disease that causes a wide range of symptoms, including fever, vomiting, joint pain, and diarrhea. Most people who get infected recover within a week or so of illness, but some develop progressive hypotension or shock, with multiorgan failure. Some patients die during the second week of illness.
EVD outbreaks are caused by a combination of factors. These include close proximity to susceptible populations, health care, and infection control practices. Preventive measures can limit transmission, such as using gloves and barrier precautions to prevent contact with body fluids and blood.
The Ebola virus is transmitted to humans through the direct contact with body fluids or blood of an infected person. It can also be spread through contact with infected animals. This includes non-human primates, chimpanzees, and forest antelope.
Secondary interventions, such as vaccination, containment of the infected population, and safe burial of dead cases, may limit transmission. However, the effectiveness of interventions in controlling EVD remains uncertain.
In an effort to better understand the dynamics of transmission of EVD, researchers performed a series of studies on the transmission of the virus. They mapped the distribution of cases at the level of chiefdoms, determining the number of contacts with infected persons before the onset of symptomatic illness.
Tertiary Interventions
Since the first outbreaks of Ebola virus disease (EVD) in 1976 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), many efforts have been undertaken to identify treatments and vaccines. Most recently, the West African epidemic accelerated efforts to explore vaccines and therapies. Nevertheless, the scale of the ongoing EVD outbreak reflects the urgent need for new treatment options.
In order to understand the dynamics of EVD, it is important to determine the highest risk populations. To do so, researchers mapped the spatiotemporal distribution of cases at chiefdom level.
During the early stages of the EVD epidemic, there were high numbers of healthcare workers infected with the virus. However, this proportion gradually decreased. Despite this, there were still a large number of health care workers infected in late 2014 and early 2015.
The number of confirmed and suspected EVD cases peaked in early November 2014. Following a case isolation campaign, the epidemic began to decline. Throughout December, transmission rates decreased significantly.
However, the effective reproduction number (CFR) was high, indicating that there may be more sporadic outbreaks of EVD in the future. Among the three most affected countries, Ebola Zaire’s CFR was 70%. Similarly, Marburg’s CFR was 80%.
Healthy People 2030 Objectives
The fifth iteration of the Healthy People initiative, Healthy People 2030, offers a lot more than a set of health goals and objectives. It provides a framework and foundational principles to guide progress over the next 10 years.
The objectives are grouped into three categories. First, there are the overarching goals. These include improving population health, reducing preventable disease, and strengthening health literacy. There are also the more practical goals.
Health departments have a variety of ways to accomplish these goals. For example, they can develop emergency operations plans, enlist help from a slew of external experts, and implement a wide variety of cross-sector partnerships. They can also pursue innovation through collaborations with their local communities.
However, there are also many other important factors to consider. For instance, health departments can improve their performance by implementing a better strategy for addressing the needs of their local communities.
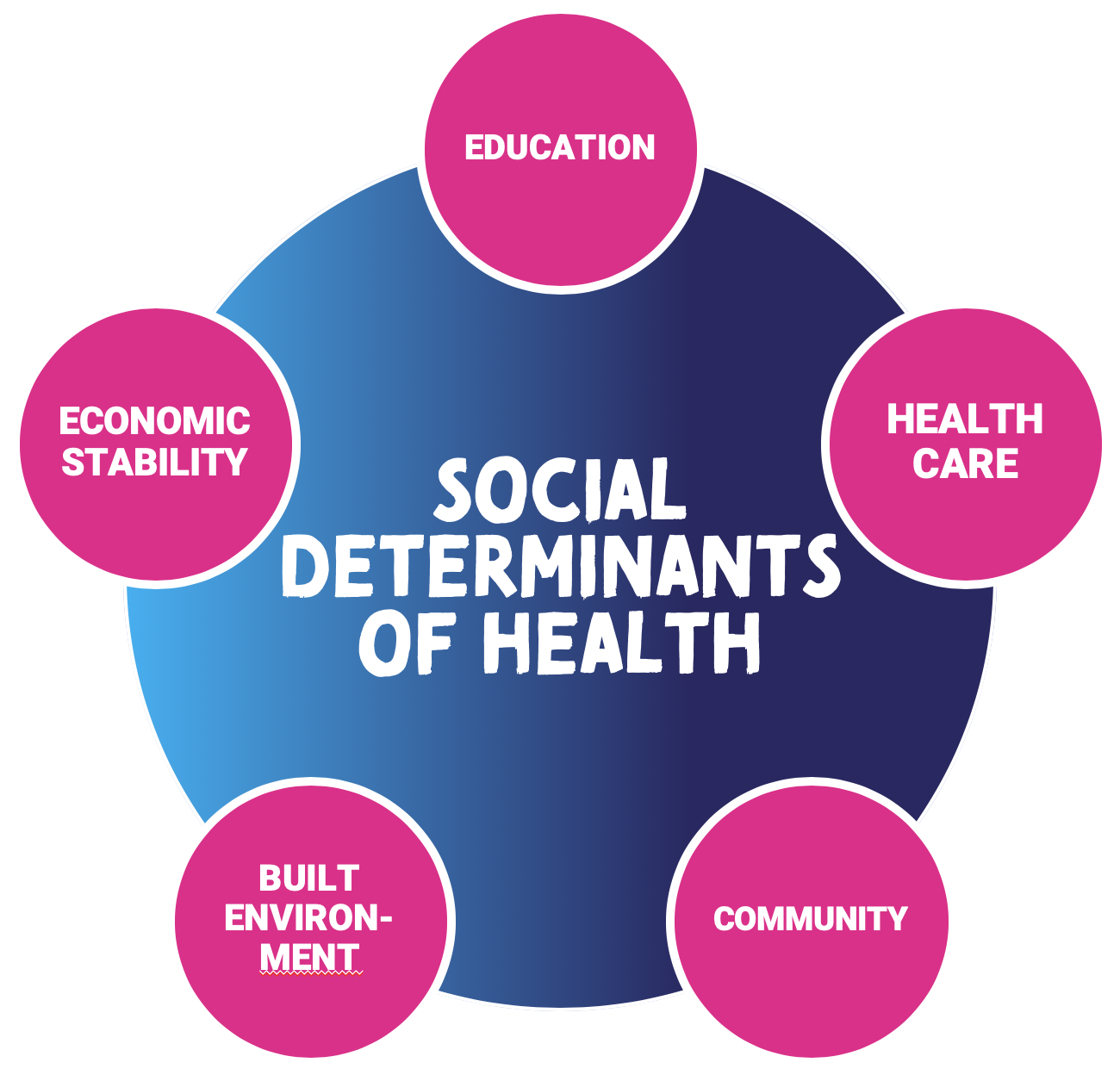
Another example is to consider the role of social determinants of health. Those in lower-income communities are more likely to suffer from chronic diseases.
Conclusion/Recommendation
The Ebola virus has been responsible for the death of thousands of people. Since its discovery, the disease has spread across many countries in Africa. This has led to a series of outbreaks. These outbreaks have affected many countries in Africa, including Guinea, Sierra Leone, DRC, South Sudan, Uganda, Nigeria, and Mali.
The 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak is one of the largest outbreaks in Africa in recent history. Over ten thousand people died in the outbreak. It began in Guinea in 2014 and spread to other countries. Some of the key factors involved in this epidemic were poor health infrastructure and weak surveillance.
A rapid case response is crucial in ending EVD outbreaks. For this, effective coordination and surveillance are needed. In addition, a strong workforce is required to respond to the epidemic. Moreover, long-term investments in improving surveillance are needed.
To end EVD, international collaboration is needed. Specifically, this includes strengthening health systems and establishing operational surveillance. Furthermore, it is necessary to improve work safety in hospitals.
Ebola is transmitted through close contact with an infected person. This is especially true for health workers, who often contract the virus while treating suspected cases. However, it can be prevented by observing good hygiene, wearing personal protective equipment, and separating healthy individuals from sick ones.












 proved job satisfaction
proved job satisfaction









 hts for information
hts for information