Social determinants of health are the conditions in the social environment that affect a person’s health status. They include factors such as health beliefs, physical environment, poverty, education, and access to health care. These factors influence the way people behave and make choices.
Introduction
One of the key determinants of health is the social and economic environment. Studies suggest that the social and economic environment are largely responsible for the majority of health outcomes.
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) includes the social determinants of health in their population health model. They are also used in the County Health Rankings model. Social determinants influence health across the life span.
To achieve optimal health, we must address the social determinants of health. This is because people’s health is influenced by a variety of factors including the distribution of resources and social and cultural determinants.
A growing number of initiatives have been launched to improve health-related social needs through the health care system. These initiatives are driven by the broader shift towards a systems approach where care is delivered through integrated delivery models.
One of the most recent examples of this is the Affordable Care Act. This legislation created an opportunity for millions of Americans to gain access to coverage. It also reduced disparities for historically underserved populations. However, this was not enough to fully achieve health equity.
Social determinants of health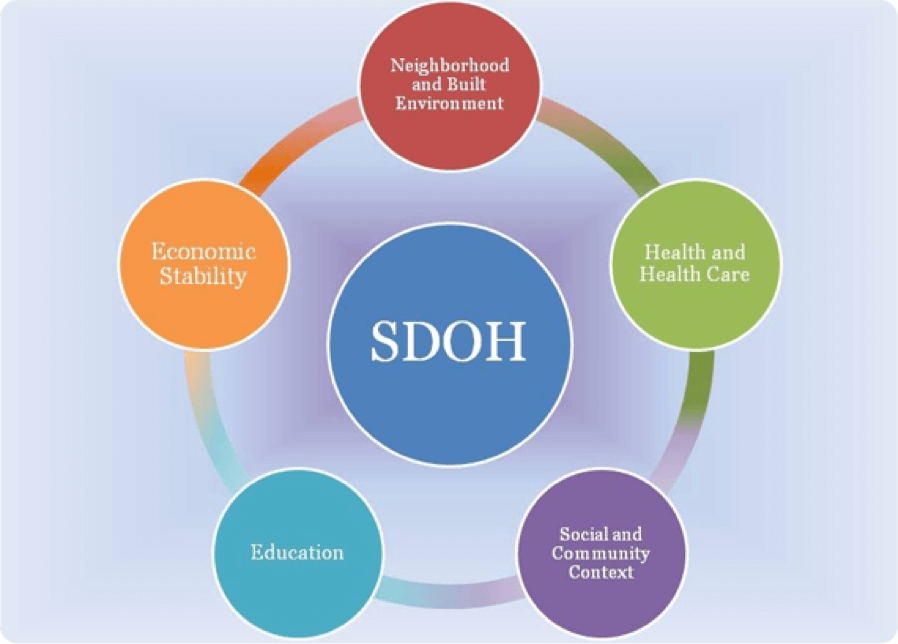
The social determinants of health (SDH) are conditions that influence the health and well-being of people. These include the quality of food, housing, educational opportunities, and transportation. Social determinants are also influenced by political and cultural policies.
In the United States, a person’s economic status affects their health. For example, people who have a higher income are healthier than those with less money. However, extreme disparities in income can also have negative effects on health.
Poor neighborhoods are more likely to have unsafe living environments, and lack of access to grocery stores with healthy food can raise health concerns. Additionally, a lack of educational opportunities can result in food insecurity. Moreover, incarceration rates and discrimination can impact children’s development.
A number of initiatives have been developed to address the social determinants of health. One such campaign, Healthy People 2030, aims to improve access to high quality education and social support for individuals. It also seeks to reduce anxiety and depression among individuals.
Another study found that states with greater social service allocation had better health outcomes than those with lower allocations. Similarly, those with higher allocations had higher rates of healthy eating, low cancer and asthma incidences, and better rates of myocardial infarction.
Impacts of social determinant of health
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines social determinants of health as “conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age.” They are important for a healthy life and have a significant impact on quality of life, medical care, and health inequities.
Social determinants of health include factors such as employment and education, as well as social support networks, housing and neighborhood conditions, and the physical environment. These are often interwoven.
Social determinants of health can be strengthened through government action. A recent study by the National Center for Biotechnology Information shows that states with a high ratio of social service spending have better health outcomes than those that don’t.
The Affordable Care Act introduced a health care system with coverage expansions and improved access to care for millions of Americans. However, these initiatives alone are not enough to improve health.
Studies show that income and social service allocation are linked to many health indicators. For example, those with higher social service allocations have lower rates of myocardial infarction, heart disease, and cancer. Additionally, states with greater social service spending outperform counterparts in obesity and mental health.
PCC and health beliefs
The PCC and health beliefs as social determinants of health brief provides an overview of the concepts and evidence for PCC and health beliefs. It includes the key components that influence the delivery and assessment of PCC.
For example, a PCC risk assessment includes an evaluation of the obstetric and gynecologic histories of past patients. This is followed by an evaluation of a physical examination.
Other components include participation in care planning and promoting self-care. These are aimed at increasing the quality of care delivered. Using a multidisciplinary approach to teach these skills is important.
The study is limited by the small sample size. However, it does show that good PCC practice is relatively common among primary healthcare nurses. There was a slight decrease in good practice as participants aged.
Participants were less likely to engage in good practice if they were female. However, it is possible that good practice is less common among females because of their age and job responsibility. Similarly, participants from rural areas showed lower levels of PCC.

Nursing care approaches
As health care professionals, nurses are tasked with addressing social determinants of health. These factors influence people’s physical, mental, and social health. They are often more important than lifestyle choices. Aside from treating illness, healthcare providers can address social determinants through five approaches.
A comprehensive approach is necessary to reduce negative health outcomes associated with these factors. This includes integrating considerations of health into government policies and community planning. It also involves institutional involvement, improved interpersonal communication, and a robust research agenda.
Healthcare organizations can address social needs through the use of community-based participatory models. Community-based approaches identify social determinants in the context of community members’ lives and encourage healthy behaviors. For example, local planning commissions consider where schools are located, where low-income housing is located, and where safety is provided.
Another approach is advocacy. The Trump Administration has outlined new policies that could limit access to assistance programs. While these initiatives aim to address health inequities at the community level, further collaboration is needed to improve access to specialty services for disadvantaged patients.
Holistic models of health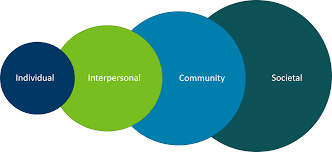
A holistic health model is one that considers the physical, mental and spiritual aspects of wellness. This approach is rooted in ancient healing traditions and is incorporated into both conventional and traditional medicine.
Unlike the medical model, which emphasizes the prevention and treatment of physical diseases, a holistic approach views well-being as a whole. By acknowledging the holistic dimensions of a person, it encourages the recognition of a person’s wholeness.
According to the World Health Organization, social determinants of health are the conditions and factors of a person’s life that influence their health. These can include economic policies, environmental conditions, social policies, political systems and development agendas.
Healthcare industry leaders are increasingly recognizing the importance of social determinants. They are positioning themselves to address health inequities and move toward value-based models.
In addition to promoting superior patient care, addressing social determinants can contribute to better health outcomes in the long-term. In fact, a recent study by the National Center for Biotechnology Information found that states with higher social service spending have better health outcomes than counterparts.
Bi-psycho social determinant of health
The bi-psycho social determinant of human health is more than just the good old fashioned ye olde hospital. It is not just the nurses and medical personnel that suffer from a host of ailments that require a bit of TLC, and in some cases, a lot of booze and a bit of yumpao. The best of the best in my experience is a healthy balance between the aforementioned components.
This is a great time to catch up with a friend for a well-deserved drink or two. Having a good time is the best way to avoid a major hiccup. So, how do you make your tee time? Here are a few tips and tricks to keep your tee time in top form: Drink responsibly!, Ensure you are drinking the right beverage, Do not slug your aforementioned partner with the bottle, Keep your aforementioned partner in good spirits, and finally, Ensure you are reserving a seat for a good time!

Conclusion
Social determinants of health are those factors that influence people’s health. In order to improve health and reduce disparities, it is essential to understand and address these.
Individuals’ lifestyles, living environment and social structures impact health. These factors may lead to long-term health inequalities. Some interventions are designed to address these social determinants. They aim to promote healthy people and healthy communities.
The US economy loses about $309 billion annually due to disparities. One in 10 Americans does not have health insurance. Another 1 in 10 does not have a primary healthcare professional.
Poor economic circumstances affect health throughout life. For example, low SES has been linked to shorter lifespans and increased rates of disability. Children of parents who do not have a high school diploma are more likely to live in substandard housing. People who live in unsafe neighborhoods are more likely to suffer from discrimination and poor health.
Gender is another major social determinant of health. Studies of gender reveal the complexities of social structure. There are questions about the extent to which the power differentials between men and women impact the health of girls and women.
PCC writing essay writing
Nursingresearchhelp.com offers:
High quality work
Samples of our previous work
24*7 customer service
Free and unlimited revisions
We are super sensitive to deliver your work before the deadline.
Why waste 10 hours to write while you can hire us to write a high quality and high scoring PCC nursing assignment. Now place your order with us at nursingresearchhelp.com and get the best PCC nursing assignment help.